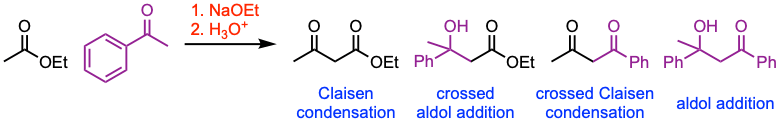
The Claisen condensation is a C–C bond-forming reaction between esters containing α-hydrogens in the presence of a strong base to give β-keto esters. If the ester enolate reacts with a ketone or aldehyde, a β- hydroxyester is formed (crossed aldol addition). Conversely, if a ketone or aldehyde enolate reacts with an ester, a 1,3-diketone is produced (crossed Claisen condensation).
- The classic Claisen condensation is a self-condensation between two molecules of a compound containing an enolizable ester.
- In the Dieckmann condensation, a molecule with two ester groups reacts intramolecularly, forming a cyclic β-keto ester.
- The reaction between two different esters is also referred to as a crossed Claisen condensation. However, this transformation can lead to four different condensation products (check experimental conditions in example 1 to determine how to minimize the formation of undesired by-products). It is generally practiced to choose one ester with no α-protons (e.g., esters of aromatic acids, formic acid, or carbonates, as seen in example 2).
Reaction mechanism of Claisen condensation
(i) The base (e.g., KOEt) deprotonates the α-proton of the ester to generate an ester enolate. (ii) The enolate reacts with the carbonyl group of the other ester to form a tetrahedral intermediate. (iii) This intermediate breaks down by ejecting a leaving group (e.g., EtO-) to give the final product. (iv) The α-proton in the β-keto ester is more acidic than in the precursor ester. Under basic conditions, the proton is removed to give a resonance stabilized anion. (v) Acidic workup provides the final product.

Examples and experimental procedures of Claisen condensations
Example 2: Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2022, e202101508. Open access.

Under an inert gas atmosphere, a solution of the indanone (13.5 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in dry THF (13.5 mL) was added to a suspension of CO(OMe)2 (2.0 equiv) in dry THF (65.0 mL) containing NaH (60% dispersion in mineral oil, 2.0 equiv). The mixture was heated to reflux for 3.5 h, then cooled to 23 ºC, stirred for 16.5 h, and finally acidified with aq. HCl (2.0 M, 15 mL). The resulting mixture was extracted with MTBE. The combined organic layers were dried over MgSO4, filtered, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was purified by flash column chromatography to afford the racemic β-keto ester.
Example 1: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 13547. Open access.

Solution A: A flame-dried round-bottom flask was charged with anhydrous THF (240 mL) under a nitrogen atmosphere. Diisopropylamine (1.36 equiv) was added via syringe, and the solution was cooled to -78 ºC. n-BuLi (2.45 M in hexanes, 1.36 equiv) was added, and the solution was stirred for 30 min at -78 ºC. tert-Butylacetate (1.42 equiv) was then added via syringe over 10 min, and the solution was stirred for 1 h at -78 ºC.
Solution B: A flame-dried round-bottom flask was charged with anhydrous THF (280 mL) under a nitrogen atmosphere. Ethyl 3-chloropropanoate (0.20 mol, 1.0 equiv) was then added via syringe, and the solution was cooled to -78 ºC.
After preparing the two solutions, solution A was added to solution B via a cannula using nitrogen overpressure over 30 min. The resulting solution was stirred for an additional 15 min at -78 ºC, then quenched with glacial acetic acid. The cooling bath was then removed, and the suspension was allowed to warm to room temperature. Et2O and distilled water were added, and the phases were separated. The organic phase was washed with sat. aq. K2CO3 and brine, dried over Na2SO4, and filtered. The filtrate was used directly in the following step.
Videos about Claisen condensation
Images of Claisen condensation
Online database of named reactions
Browse named reactions in alphabetical order or by category in our online database of organic reactions.


















