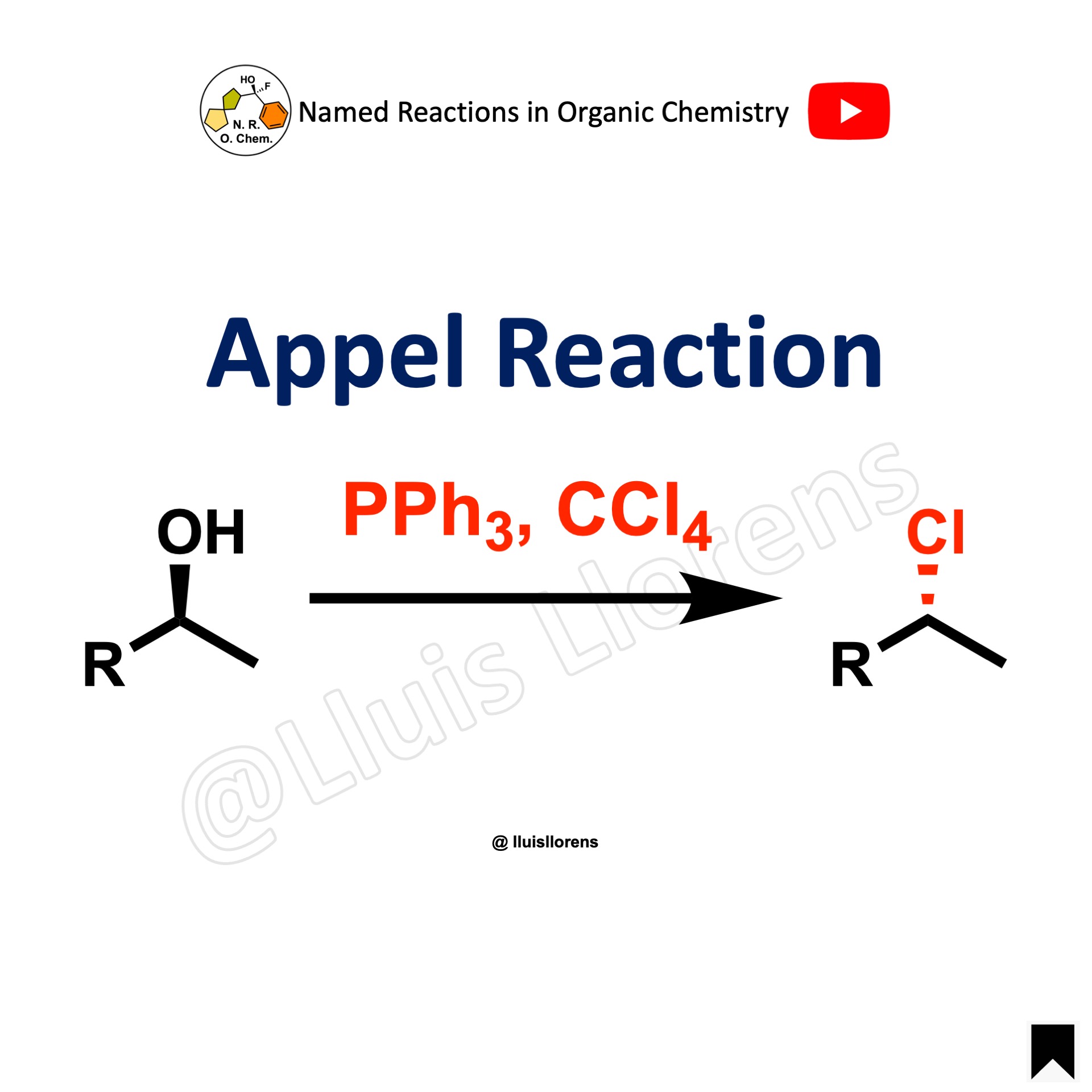
The Appel reaction allows the conversion of an alcohol into the corresponding alkyl chloride under mild conditions by the reaction of triphenylphosphine and tetrachloromethane with the alcohol.
- With primary and secondary alcohols, the halide reacts in a SN2 fashion, proceeding with inversion of configuration if the carbon is asymmetric (see example 3). Tertiary alcohols, on the other hand, form the products via a SN1 mechanism.
- In addition to the formation of alkyl chlorides, the use of carbon tetrabromide or bromine as a halide source will yield alkyl bromides (see example 1), whereas using carbon tetraiodide, or another source of iodide anions will give alkyl iodides (see example 2).
- For sustainable Appel reaction conditions see: ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 2300.
- For removal of triphenylphosphine oxide (TPPO) by precipitation with zinc chloride, see: J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 9931. Open access.
- For a catalytic Appel reaction, see: J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 6749.
- A closely related nucleophilic substitution reaction is the Mitsunobu reaction.
Reaction mechanism of Appel reaction
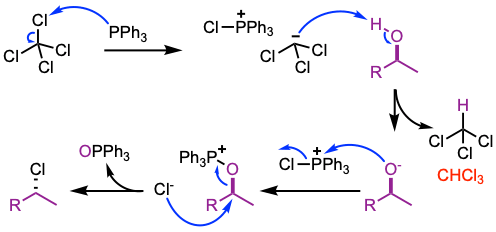
- Activation of triphenylphosphine by reaction with tetrachloromethane generates the phosphonium salt.
- Deprotonation of the alcohol yields chloroform and an alkoxide derivative.
- The alkoxide reacts with the phosphonium salt at the phosphorus centre to generate an oxyphosphonium intermediate, making the oxygen a good leaving group.
- Displacement by the halide generates the alkyl halide and triphenylphosphine oxide.
Examples and experimental procedures of Appel reactions
Example 3: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 10872. Open access.

To a flame-dried round-bottom flask, N-chlorosuccinimide (NCS, 1.05 equiv), THF (3.2 mL), and PPh3 (1.05 equiv) were sequentially added. The resulting slurry was stirred for 30 min at room temperature in the dark. The hydroxy ketone (0.83 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in THF (1.5 mL) was then added to the reaction mixture, followed by another portion of THF (1.7 mL). The resulting slurry was stirred at room temperature for 17 h. The reaction mixture was concentrated under vacuum. The resulting residue was purified by flash column chromatography to afford the alkyl chloride.
Example 2: Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 6349.

Iodine (1.5 equiv) and imidazole (3.0 equiv) were added sequentially to a solution of triphenylphosphine (1.5 equiv) in DCM (3 mL) at 0 ºC. After 10 min a solution of the (R)-alcohol (1.14 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in DCM (1 mL) was added dropwise. The reaction mixture was warmed to room temperature and stirred for 16 h before it was quenched with sat. aq. Na2S2O3. The phases were separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with DCM. The combined organic layers were dried over MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated under vacuum. The crude residue was then purified by flash column chromatography to afford the alkyl iodide.
Example 1: Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5314. Open access.
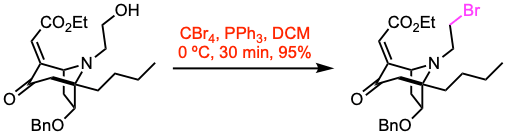
To a cooled solution (0 ºC) of the alcohol (4.60 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in anhydrous DCM (50 mL), CBr4 (1.3 equiv) and PPh3 (1.5 equiv) were added under a nitrogen atmosphere. The resulting mixture was stirred at 0 ºC for 30 min and then concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography to afford the alkyl bromide.
Videos about Appel reaction
Images of Appel reaction
Online database of named reactions
Browse named reactions in alphabetical order or by category in our online database of organic reactions.