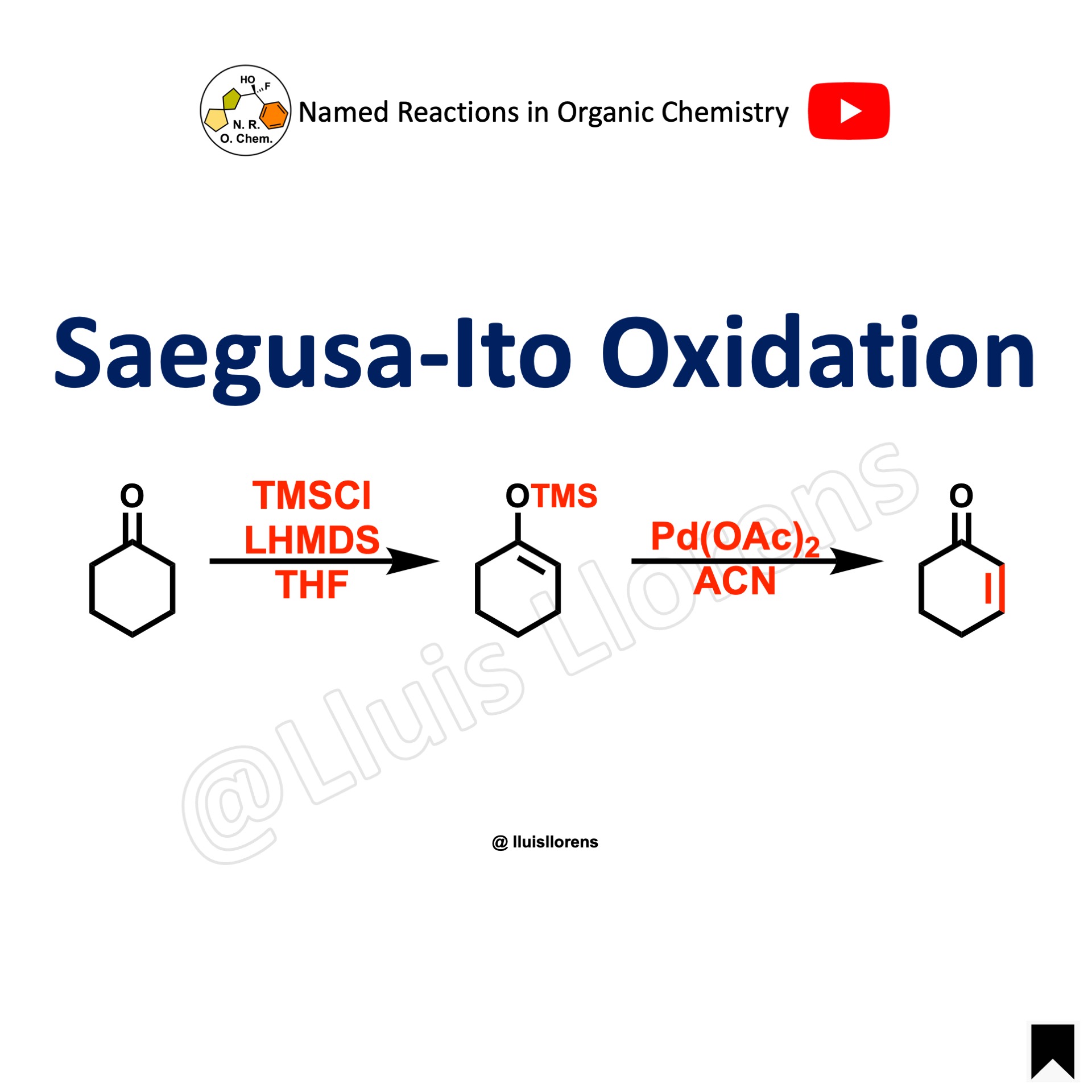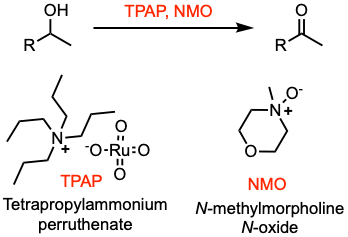
The Ley-Griffith oxidation enables the oxidation of primary or secondary alcohols to aldehydes or ketones. The central catalyst is tetra propylammonium perruthenate (TPAP), which is used in combination with the co-oxidant N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMO).
- TPAP is a solid and an air-stable compound soluble in a range of organic solvents.
- The reaction is fast, and there is a danger of explosion on a multigram scale and cooling might be necessary.
- Standard conditions: 5 mol% of TPAP, 1 equivalent of alcohol, 1.5 equivalents of NMO, DCM, room temperature, 1-16 hours, yields 70-95%.
- The presence of molecular sieves enhances the reaction rate and efficiency.
- The work-up generally involves purification by silica-gel column chromatography.
- The Ley-Griffith oxidation is an alternative to various oxidation reactions used to transform alcohols into aldehydes or ketones.
Reaction mechanism of Ley-Griffith oxidation
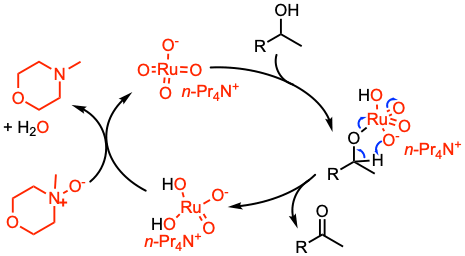
The mechanism of Ley-Griffith reaction is complex and not well-known. A suggested mechanism involves the following steps:
1. TPAP oxidizes the alcohol.
2. The TPAP–alcohol complex (ruthenate ester) rearranges to deliver the ketone.
3. NMO reactivates the catalyst.
For further details on the reaction mechanism, see: Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 8435. Open access.
Examples and experimental procedures of Ley-Griffith oxidation
Example 2: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 11811. Open access.
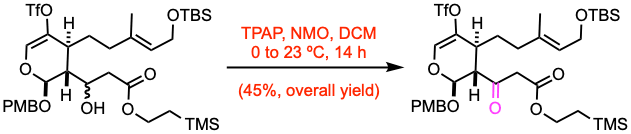
Tetrapropylammonium perruthenate (0.25 equiv) was added to a solution of the alcohol (4.81 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and N-methylmorpholine N-oxide (3.0 equiv) in DCM (45 mL) at 0 ºC. The reaction mixture was allowed to slowly warm to 23 ºC. After 14 h, the reaction mixture was filtered through a plug of silica gel. After flushing with Et2O, the filtrate was concentrated to give the crude ketoester as a mixture of keto-enol tautomers, which was used in the following step without further purification.
Example 1: Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10934. Open access.
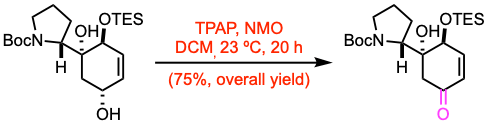
Tetrapropylammonium perruthenate (TPAP, 0.05 equiv) and N- methylmorpholine N-oxide (NMO, 6.0 equiv) were added to a stirred solution of the alcohol (0.92 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in anhydrous DCM (9 mL) at 23 ºC. After 20 h, the reaction mixture was filtered through a pad of Celite. The resulting solution was washed with sat. aq. Na2SO3 solution and 5% aq. copper sulfate solution. The combined organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. The resulting filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give the crude ketone, which was used in the next steps without further purification.
Video about Ley-Griffith oxidation
Images of Ley-Griffith oxidation
Online database of named reactions
Browse named reactions in alphabetical order or by category in our online database of organic reactions.