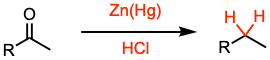
The Clemmensen reduction allows the conversion of a carbonyl group to the corresponding methylene group using zinc amalgam and concentrated hydrochloric acid.
- Due to its original harsh conditions, the Clemmensen reduction is rarely used in modern organic synthesis. Yamamura and colleagues developed another excellent modification (activated zinc and saturated HCl in Et2O at 0 ºC), eliminating the need for toxic mercury. See Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1972, 45, 264.
- Relatively milder procedures have been developed to make the synthesis appropriate for acid- and heat-sensitive compounds. Under these conditions, the reaction takes place even without pre-activation of the zinc metal (see example 1).
- For a protocol on the reductive cleavage of an exo-olefin to methylene with a mild ozonolysis-Clemmensen reduction sequence, see: Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 4534.
Reaction mechanism of Clemmensen reduction
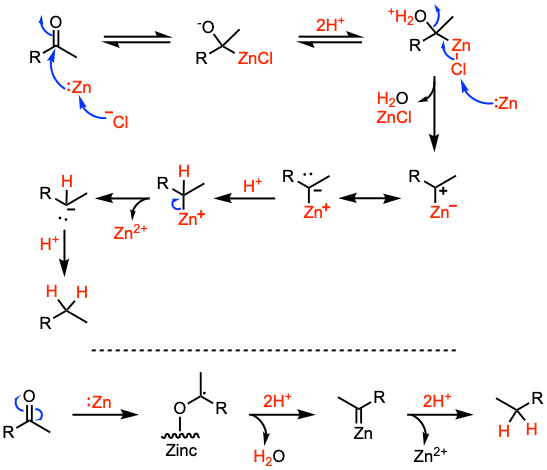
Suggested reaction mechanisms of the Clemmensen reduction via formation of a carbanion species or a carbenoid intermediate.
Examples and experimental procedures of Clemmensen reduction
Example 1: Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 3687.
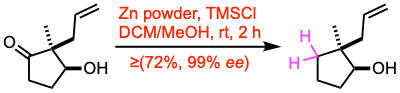
To a stirred solution of the hydroxy ketone (17.2 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and zinc powder (10.0 equiv) in DCM and MeOH (180 mL, 1:1), trimethylsilyl chloride (10.0 equiv) was added dropwise at 0 ºC. The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h. The zinc powder was removed by filtration, and the filtrate was neutralized with sat. aq. NaHCO3. The reaction mixture was then extracted with DCM, and the combined organic layer was washed with water and brine, and dried over Na2SO4. The crude product was concentrated under reduced pressure and used in the next step without further purification.
Video about Clemmensen reduction
Images of Clemmensen reduction
Online database of named reactions
Browse named reactions in alphabetical order or by category in our online database of organic reactions.