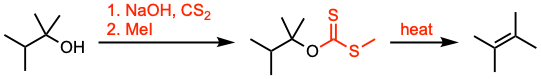
The Chugaev elimination involves the formation of olefins by pyrolysis of the corresponding xanthates derived from β-hydrogen-containing alcohols via syn elimination.
- The Chugaev elimination reaction is analogous to the thermal decomposition of carboxylic esters of alcohols, and of other related derivatives of alcohols, such as carbamates and carbonates. Xanthates typically undergo elimination from 120 to 200 °C, while esters typically require 400 to 500 °C.
- The thermolysis of xanthates is a cis-concerted elimination that occurs via a mechanism in two steps, the first one being the rate-limiting step.
- The reaction proceeds without the rearrangement of the carbon skeletons under relatively mild conditions.
- The clean formation of the alkene (in example 3) is in line with the well-accepted syn-elimination mechanism of the Chugaev elimination, as generation of a cationic intermediate would generate undesired rearrangements.
- The Chugaev elimination mainly focuses on secondary xanthates. For more stable primary xanthates, much higher temperatures (>200 °C) are required, and the yields are unsatisfactory. For more details, see Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 1659.
Reaction mechanism of Chugaev elimination

The suggested mechanism of the Chugaev elimination involves a two-step process, with an initial rate-determining step via a six-membered cyclic transition state in which the thiocarbonyl sulfur and the ether oxygen participate, followed by a rapid decomposition of the intermediate.
The initial products are the alkene and an unstable dithiocarbonate derivative which subsequently decomposes to carbonyl sulfide and a thiol.
For more details, refer to J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2008, 21, 797.
Examples and experimental procedures of Chugaev elimination
Example 3: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 24408.

A solution of KHMDS (1.0 M in THF, 1.5 equiv) was added to a solution of the alcohol (0.47 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in THF (18.5 mL) at -78 ºC. The mixture was stirred for 15 minutes at this temperature before a solution of O-phenyl chlorothionoformate (3.0 equiv) in THF (0.5 mL) was added quickly. The mixture was stirred at -78 ºC for 15 min before being quenched by the addition of sat. aq. NaHCO3. The layers were separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried over Na2SO4, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by flash column chromatography.
A solution of the thiocarbonate O-ester (0.42 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in Ph2O (16 mL, freshly degassed under 3×10 min vacuum-argon cycles) was stirred at 220 ºC for 3 h. After cooling to room temperature, THF (32 mL) was added, the mixture was cooled to 0 ºC followed by the dropwise addition of TBAF (1.0 M in THF, 3.0 equiv). After 2 h at 0 ºC the reaction mixture was poured into sat. aq. NH4Cl. The layers were separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried over Na2SO4, and the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by flash column chromatography to afford the alkene.
Example 2: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 18823.
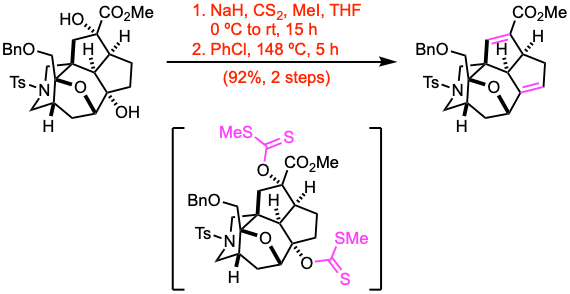
To a stirred solution of the alcohol (2.33 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in THF (30 mL) at 0 ºC was added sodium hydride (NaH, 60% dispersion in mineral oil, 25.0 equiv) over 10 minutes, the reaction mixture was stirred for 1 h at 0 ºC, carbon disulfide (CS2, 35.0 equiv) was added to the mixture. Then the reaction mixture was warmed to 25 ºC and stirred for 2 h. Then, iodomethane (MeI, 40.0 equiv) was added to the mixture, and the resultant mixture was stirred for 12 h at 25 ºC. The reaction mixture was then carefully poured into sat. aq. NH4Cl with crushed ice, and the layers were separated. The aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were washed with brine, dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was passed through a short silica gel column. The eluate was concentrated to give the xanthate, which was used without further purification. The xanthate was dissolved in chlorobenzene (PhCl, 30 mL), the stirred solution was heated at 148 ºC to reflux for 5 h. Then the mixture was cooled down to 25 ºC, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography to give the alkene.
Example 1: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 4592.

To a stirred solution of the alcohol (50 μmol, 1.0 equiv) and CS2 (4.0 equiv) in THF (5 mL) at 0 ºC, NaH (60% dispersion in mineral oil, 4.0 equiv) was added. The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature for 5 h before MeI (4.0 equiv) was added. The reaction mixture was stirred for an additional 10 min before it was quenched with NH4Cl. The layers were separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under vacuum to afford the crude product.
A stirred solution of the xanthate (crude product obtained above) in o-DCB (5 mL) was warmed to 150 oC and stirred for 20 h before it was cooled to room temperature. Then, MeOH (5 mL) and p-TsOH·H2O (2.0 equiv) were added. The resulting mixture was warmed to 30 ºC and stirred for 36 h before it was diluted with EtOAc and quenched with NaHCO3. The layers were separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4 and concentrated under vacuum. Flash column chromatography afforded the desired alkene.
Videos about Chugaev elimination
Images of Chugaev elimination
Online database of named reactions
Browse named reactions in alphabetical order or by category in our online database of organic reactions.