The Chan-Lam coupling is the cross-coupling reaction between an aryl boronic acid and an amine or alcohol to generate the corresponding secondary aryl amine or ether.

- In contrast to other cross-coupling reactions, the Chan-Lam reaction is unique in that it couples two nucleophiles: an aryl organoboron compound and an amine (see example 2) or alcohol (see example 1 and example 3).
- Typical substrates: phenols, amines, anilines, amides, imides, ureas, carbamates, sulfonamides, sulfoximes, and NH-heterocycles.
- Cu source: Cu(OAc)2, Cu(OTf)2, Cu(OPiv)2, Cu(acac)2, Cu(TFA)2, CuBr2, CuCl2, CuSO4, CuFAP, [Cu(DMAP)4I]I, [Cu(OH)·TMEDA]2Cl2, Cu(MeCN)4PF6, CuCl, Cu2O, Cu2S.
- Oxidant: O2(air), O2, pyridine N-oxide, TEMPO, (t-BuO)2.
- Base: Et3N, (i-Pr)2NEt, pyridine, 4-methylpyridine, 2,6-lutidine, K2CO3, K3PO4, KOt-Bu, N-methylpiperidine, n-Bu4NOH, NaOSiMe3, none.
- Solvents used: CH2Cl2, MeCN, EtOAc, MeOH, EtOH, 1,4-dioxane, NMP, THF, DMF, PhMe, DMSO, H2O, t-BuOH.
- Temperature range: rt to 100 °C.
- For synthetic applications of the Chan-Lam coupling, see: Mol Divers 2019, 23, 215 and Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 3311.
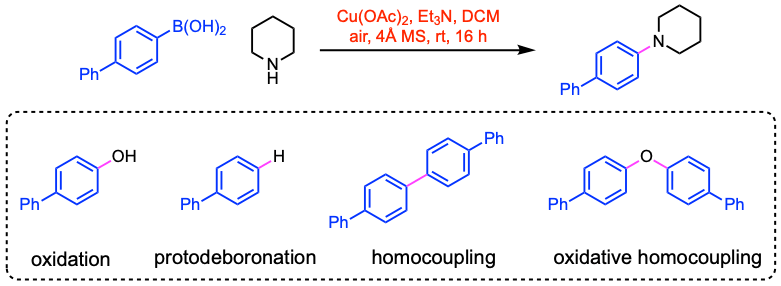
The utility of the Chan-Lam amination is often hampered by significant problems with by-product formation. Some by-products include the oxidation product, the protodeboronation product, or the homocoupling of the organoboron component.
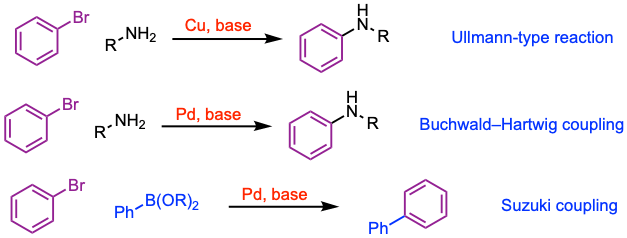
The Chan-Lam coupling can be viewed as a combination of the Suzuki coupling, which involves the aryl boronic component, and the Buchwald-Hartwig reaction, which involves the amine component. Unlike these reactions, which are catalyzed by palladium, the Chan-Lam coupling typically uses a catalytic or stoichiometric amount of copper, and the reaction can be conducted in air and at room temperature. It also bears resemblance to the Ullmann-type reaction, a copper-catalyzed nucleophilic aromatic substitution between nucleophiles such as amines and aryl halides. However, Ullmann-type couplings often require harsh conditions, such as high temperatures or strong bases.
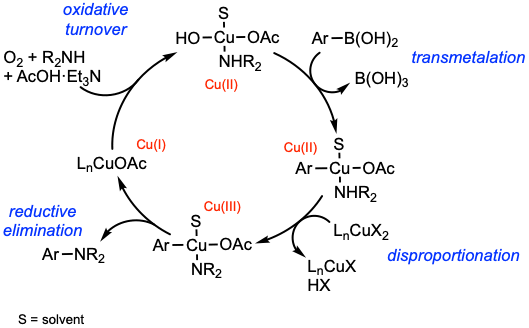
Reaction mechanism of Chan-Lam coupling
A suggested general mechanism of the Chan-Lam coupling is presented. Transmetalation of the organoboron compound, here a boronic acid, delivers a Cu(II) complex. Disproportionation using a second Cu(II) delivers the key Cu(III) complex. Reductive elimination forges the C–N bond, liberating the product and a Cu(I) species. Oxidative turnover of Cu(I) to Cu(II) using a terminal oxidant, most commonly O2, completes the catalytic cycle. For mechanistic aspects of the Chan-Lam coupling, see: Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 7735 and Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 12491.
Examples and experimental procedures of Chan-Lam coupling
Example 3: Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 2022.

To a stirred solution of the boronic ester (10.9 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in DCM/MeOH (109 mL, 1:1) at room temperature, 4Å molecular sieves (activated, 6.0 g), Cu(OAc)2 (1.0 equiv), and DMAP (2.0 equiv) were added. The resulting mixture was stirred for 8 h before it was filtered through a pad of silica gel, eluted with EtOAc, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was purified by flash column chromatography to afford the coupled product.
Example 2: New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 308.
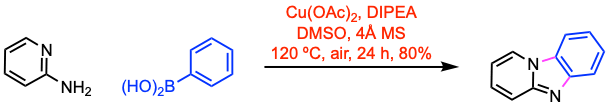
Example 1: J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 3417.

Videos about Chan-Lam coupling
Images of Chan-Lam coupling
Online database of named reactions
Browse named reactions in alphabetical order or by category in our online database of organic reactions.