The Baeyer-Villiger oxidation allows the transformation of ketones into esters and cyclic ketones into lactones by the use of a wide range of peroxyacids, being m-CPBA the most common. The regiochemistry depends on the migratory capacity of the alkyl groups, with the more branched group generally migrating faster.

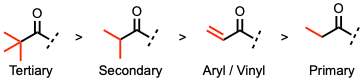
- The Baeyer-Villiger (BV) reaction tolerates the presence of many functional groups in the ketone.
- The regiochemistry depends on the migratory capacity of the alkyl groups.
- The rearrangement step occurs with retention of configuration (see example 3).
- A wide range of peroxyacids can be used being m-CPBA the most common.
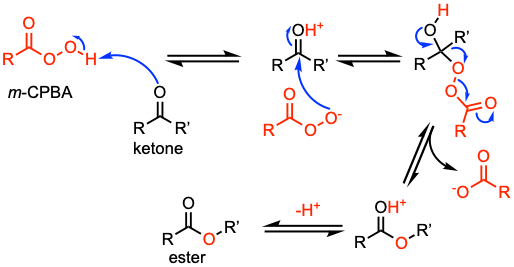
Reaction mechanism of Baeyer-Villiger oxidation
A suggested mechanism of the BV oxidation. (i) m-CPBA protonates the oxygen of the ketone. (ii) The peroxyacid adds then to the more electrophilic carbonyl carbon. (iii) Formation of a “Criegee intermediate.” (iv) One of the substituents from the ketone migrates to the oxygen of the peroxide group. (v) Deprotonation leads to the ester. For further details, see Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 646 and Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4105.
Examples and experimental procedures of Baeyer-Villiger oxidation
Example 3: Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 1941.

A solution of the ketone (7 mmol, 1.0 equiv) in DCM (70 mL) was treated with m-CPBA (85%, 2.0 equiv). The mixture was stirred at 45 ºC for 48 h. The mixture was quenched by the addition of sat. aq. Na2S2O3, diluted with sat. aq. NaHCO3, and extracted with DCM. The combined organic phases were dried over Na2SO4. After filtration, the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was purified by flash column chromatography.
Example 2: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 12970.

Example 1: Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 14967.

To a stirred ice-cold solution of the ketone (2.50 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and m-CPBA (2.6 equiv) in dry DCM (25 mL), TFA (1.0 equiv) was added. The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 h. After that, the reaction mixture was quenched by the addition of sat. aq. NaHCO3 and extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic layers were dried over Na2SO4, filtered, and evaporated to dryness. The resulting material was used in the next step without further purification.
Video about Baeyer-Villiger oxidation
Images of Baeyer-Villiger oxidation
Online database of named reactions
Browse named reactions in alphabetical order or by category in our online database of organic reactions.