The Barton-McCombie reaction is a deoxygenation reaction in which a hydroxy-functional group in an organic compound is replaced by a hydrogen atom to give an alkyl group. The alcohol is first transformed into a thioxoester that is then exposed to n-Bu3SnH and AIBN in refluxing toluene.

- The Barton-McCombie deoxygenation is one of the first methods that comes to mind for most chemists if thinking about the chemoselective and mild removal of a hydroxy group. The reaction involves the conversion of the hydroxy group into a suitable leaving group, which is then removed in the second step.
- The use of stannanes as the hydride source for deoxygenation entails disadvantages, as they are toxic and difficult to remove from the reaction mixture.
Reaction mechanism of Barton-McCombie reaction
A suggested reaction mechanism of the Barton-McCombie reaction: (i) The alcohol is first converted into a thioxoester or xanthate ester. (ii) Homolytic cleavage of AIBN generates the radical species that abstracts a hydrogen atom from tributylstannane. (iii) The tributylstannyl radical abstracts the xanthate group. (iv) The resulting alkyl radical abstracts another hydrogen atom from tributylstannane, generating the deoxygenated product and a new radical species.

Examples and experimental procedures of Barton-McCombie reaction
Example 2: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 15475.

Note: CS2 was dried over CaCl2 overnight prior to its use. A flame-dried two-necked round-bottom flask equipped with a stirring bar was charged with anhydrous THF (94.0 mL) and the substrate (10.7 mmol, 1.0 equiv). The solution was cooled to -78 ºC with a dry ice/acetone bath and CS2 (20.0 equiv) was added, followed by the dropwise addition of NaN(SiMe3)2 (1.0 M in THF, 1.4 equiv) over 5 minutes, which resulted in a color change to an intense red. After complete addition, the mixture was stirred for 10 min at -78 ºC and for 1 h at -45 ºC. After this time the now orange mixture was cooled back to -78 ºC, MeI (15.0 equiv) was added dropwise, and the resulting mixture was stirred for 5 h at -78 ºC. The reaction was quenched at -78 ºC with sat. aq. NH4Cl, the layers were separated, and the aqueous phase was extracted with Et2O. The combined organic layers were dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated in vacuo. Purification by silica gel column chromatography provided the S-methyl carbonodithioate.
Note: AIBN was freshly recrystallized from Methanol at 50 ºC. A flame dried Schlenk tube equipped with a stirring bar was charged with AIBN (0.50 equiv), toluene (83.0 mL), the S-methyl carbonodithioate (8.32 mmol, 1.0 equiv), and n-Bu3SnH (5.00 equiv). The septum was switched for a glass stopper, and the yellow solution was heated to 105 ºC. After 3 h the reaction was allowed to cool to room temperature. The mixture was concentrated in vacuo without a workup. Purification by silica gel column chromatography provided the product.
Example 1: Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 3313.
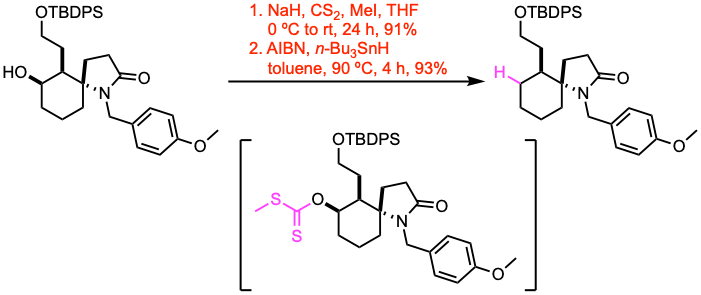
A two-necked round-bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirring bar, a rubber septum, and an inlet adapter with a three-way stopcock was charged with the alcohol (1.28 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and dry THF (16 mL). After the addition of NaH (60% oil dispersion, 1.5 equiv) to the solution at 0 ºC, the resultant mixture was stirred at 0 ºC for 30 min, and CS2 (5.0 equiv) was added at 0 ºC. After stirring for an additional 1 h at room temperature, MeI (5.0 equiv) was added, and stirring was continued at room temperature for 24 h. Then, the reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure to give a crude material, which was purified by flash column chromatography to afford the S-methyl carbonodithioate.
A round-bottom flask equipped with a magnetic stirring bar and an inlet adapter with a three-way stopcock was charged with the substrate (1.15 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and dry toluene (80 mL). To the solution, AIBN (0.2 equiv) and n-Bu3SnH (2.0 equiv) were added at room temperature. The reaction mixture was stirred at 90 ºC for 4 h, until complete consumption of the starting material. The reaction mixture was quenched with sat. aq. NH4Cl. The reaction mixture was then extracted with EtOAc. The combined organic extracts were washed with brine, dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure to give the deoxygenated product, which was purified by flash column chromatography.
Videos about Barton-McCombie reaction
Images of Barton-McCombie reaction
Online database of named reactions
Browse named reactions in alphabetical order or by category in our online database of organic reactions.