Strecker Synthesis
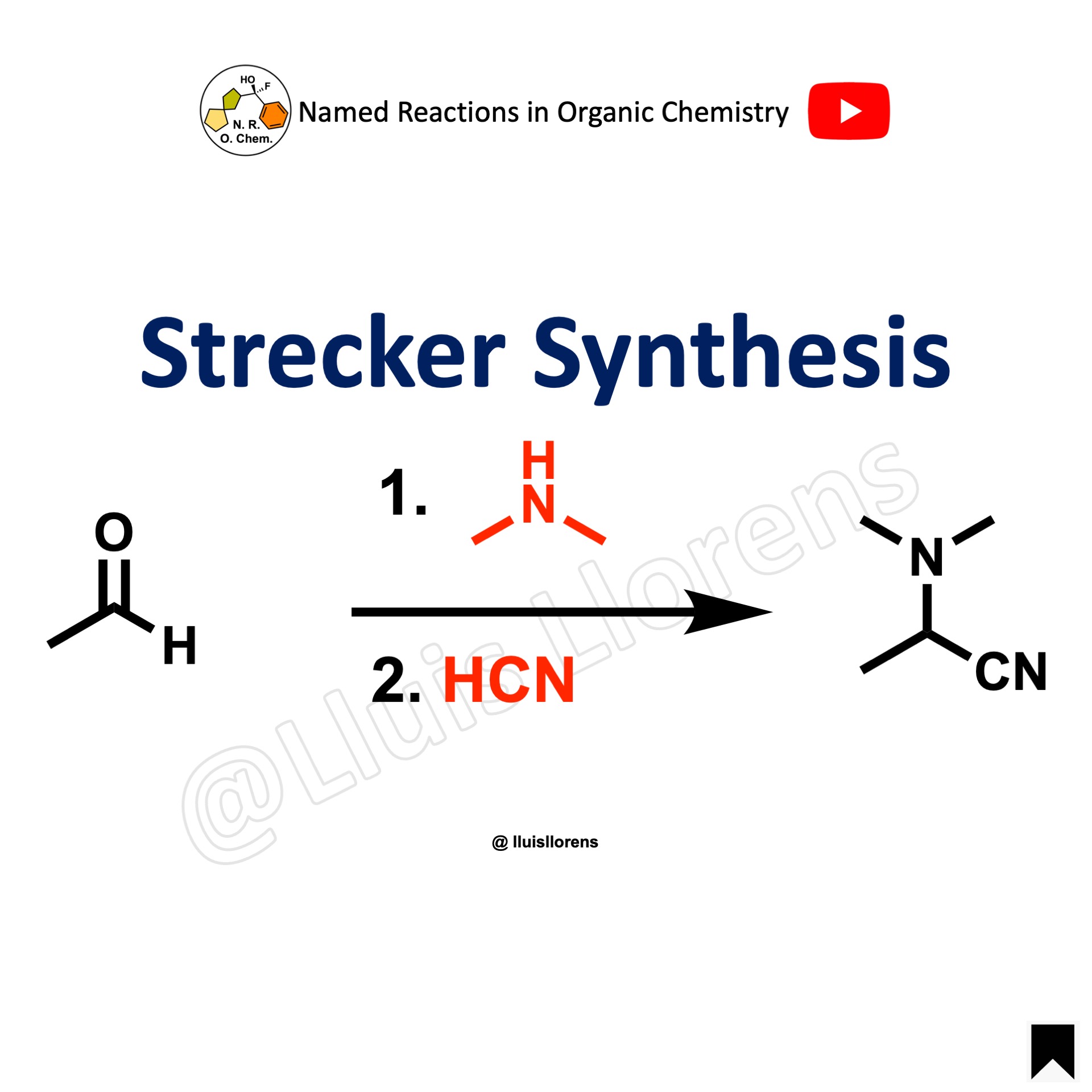
The Strecker reaction is the condensation of an aldehyde or ketone with a primary amine or ammonia and hydrogen cyanide to afford the corresponding alpha-aminonitrile.
General features:
1. The α-amino nitriles are often hydrolyzed under acidic or basic conditions to obtain α-amino acids. 2. To avoid the use of highly toxic HCN, various cyanides (KCN, NaCN) in buffered aqueous media are used. 3. Reduction of the corresponding α-amino nitriles with metal hydrides affords 1,2-diamines.
Reaction Mechanism
1. Condensation of ammonia/amine with the aldehyde/ketone. 2. Formation of an iminium ion. 3. Addition of the cyanide to the iminium ion carbon. 4. Further hydrolysis leads to the corresponding aminoacid.
Experimental Procedure
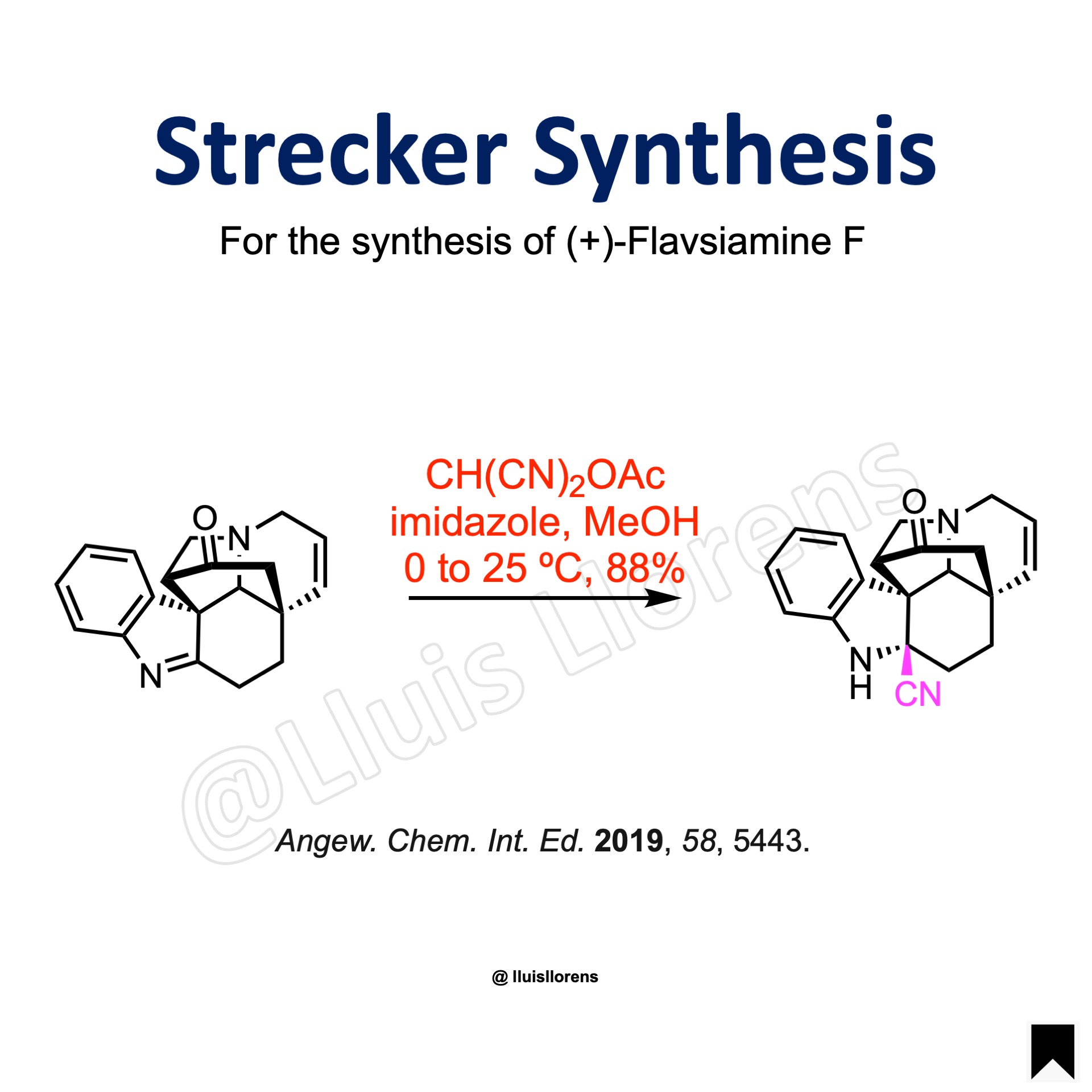
To a solution of the imine (0.09 mmol, 1.0 eq) in anhydrous MeOH (2 mL) was added imidazole (2.5 eq) and CH(CN)2OAc (1.1 eq) at 0 ºC under an atmosphere of Argon. After stirring at room temperature for 1 h, the reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure and purified by flash chromatography to afford the corresponding nitrile (88% yield).
Lab Experiment
Learn More Named Reactions
[instagram-feed feed=2]