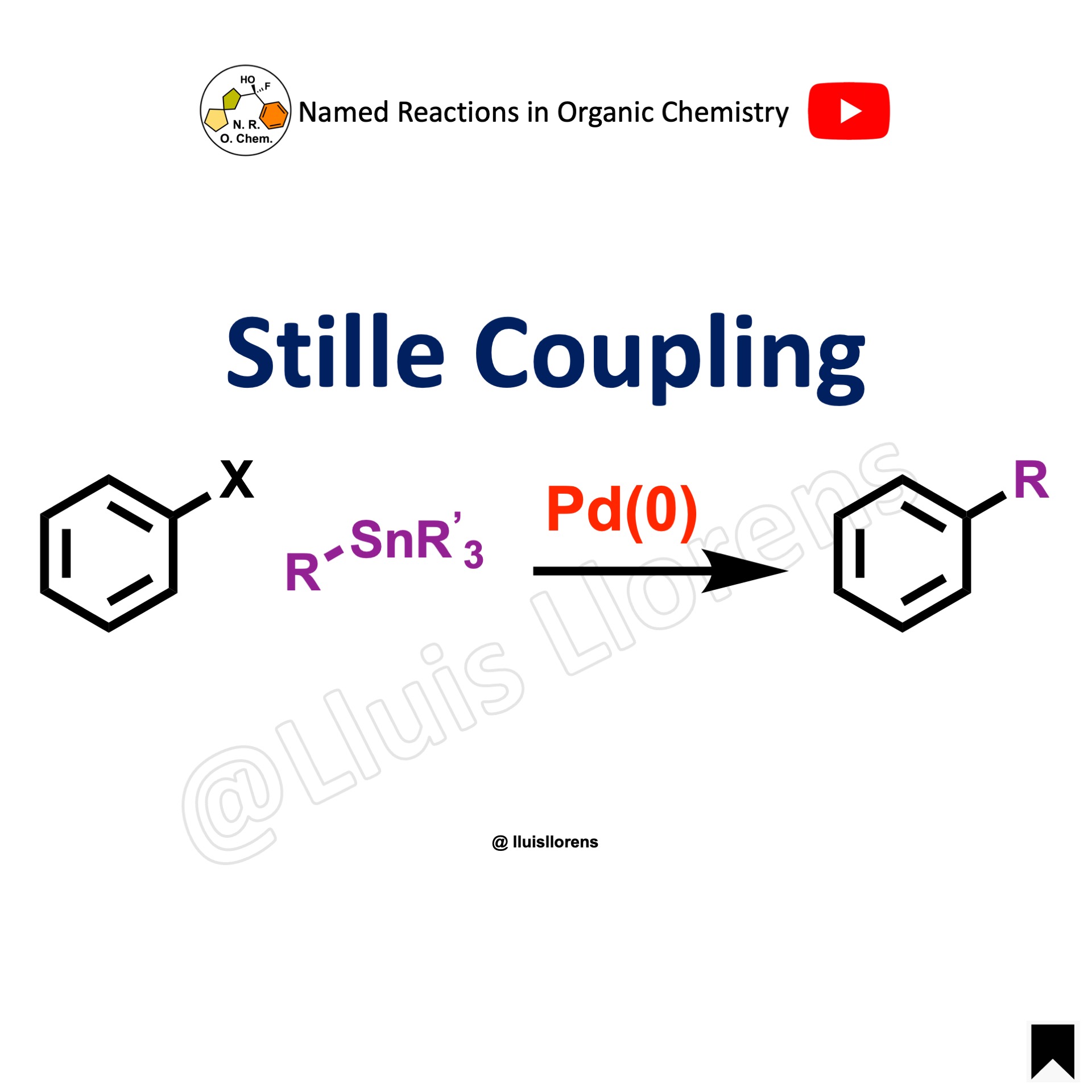
Stille Coupling
The Stille cross-coupling is the palladium-catalyzed reaction between stannanes and halides to generate a C–C bond.
General features:
1. The organotin reagents tolerate a wide variety of functional groups and are not sensitive to moisture or oxygen. Besides, they can be easily prepared, isolated, and stored. However, they are toxic and difficult to remove from the reaction mixture. 2. The reaction requires mild conditions to take place. 3. The major side reaction that may occur is the oxidative homocoupling of the organostannane. 4. Work-up: In many Stille reactions, the Bu3SnX by-products can be removed by filtering through silica made up with ~2-5% triethylamine in the eluent. Other methods include washing the reaction mixture with a saturated aqueous solution of KF.
Reaction Mechanism
1. Oxidative addition of an organic halide to Pd(0) to form Pd(II). 2. Transmetalation between Pd(II) and the organotin reagent. 3. Reductive elimination to form the C–C sigma bond and regeneration of the catalyst.
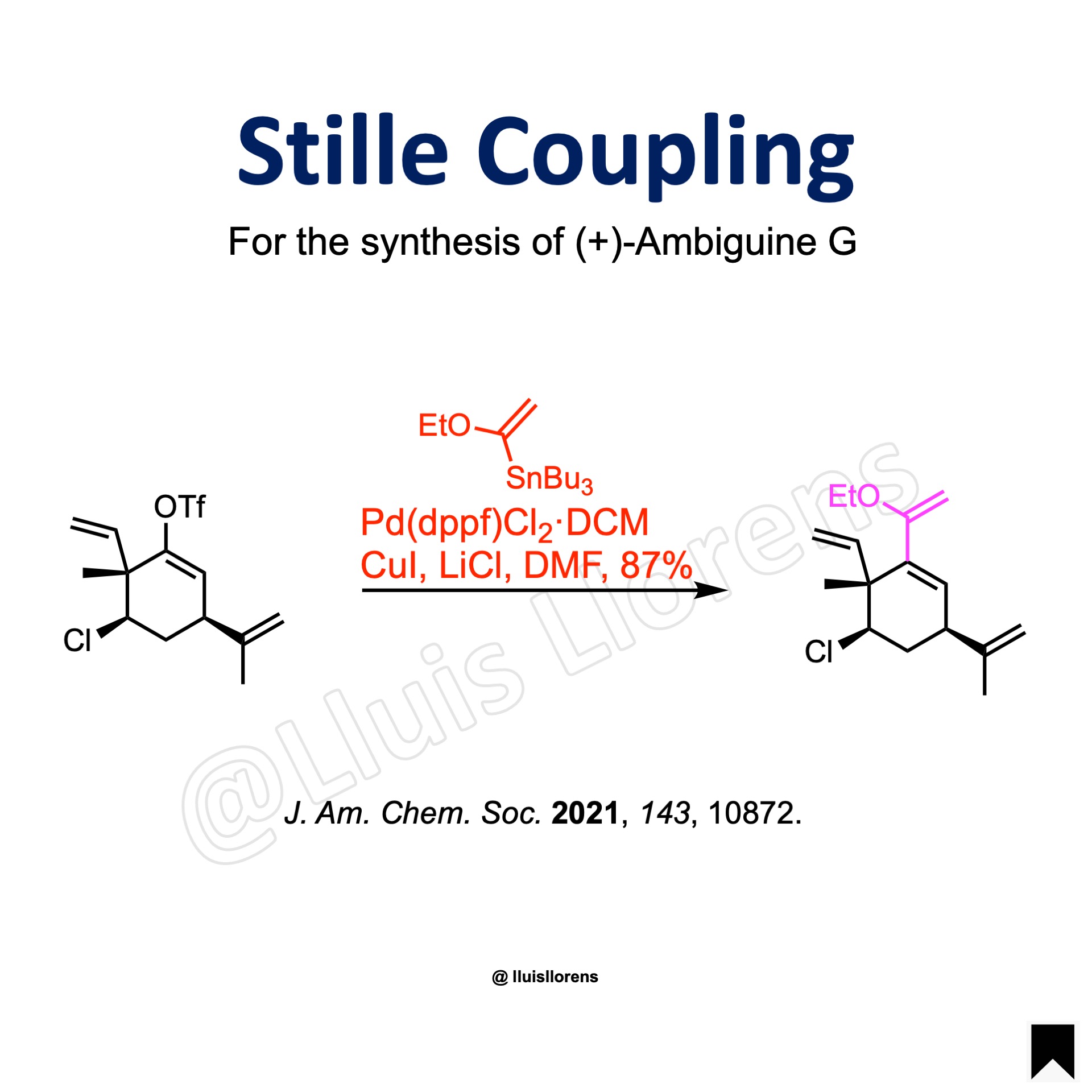
Example
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 10872. (OPEN ACCESS)
Experimental Procedure
To a flame-dried 100 mL round-bottom flask was added the enol triflate (4.60 mmol, 1 eq) and DMF (bubbled with N2 for 45 min before use, 35 mL). CuI (0.1 eq), Pd(dppf)Cl2·DCM (0.1 eq), and LiCl (5.3 eq) were added sequentially. Another 11 mL of DMF was added to make a 0.1 M solution. The reaction flask was purged with Ar for 10 min before the addition of the organotin reagent (1.15 eq). The solution was then heated to 40 °C. After 2.5 days at 40 °C, the brown solution was transferred into a separatory funnel containing NH3·H2O:H2O 1:2, which was extracted with hexane. The organic phase was combined and washed with NH3·H2O:H2O 1:2 and brine, dried over Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated in vacuo. The crude material was purified by flash chromatography (basic alumina) to afford the coupled product (87% yield).
Learn More Named Reactions
[instagram-feed feed=2]