Saegusa-Ito Oxidation
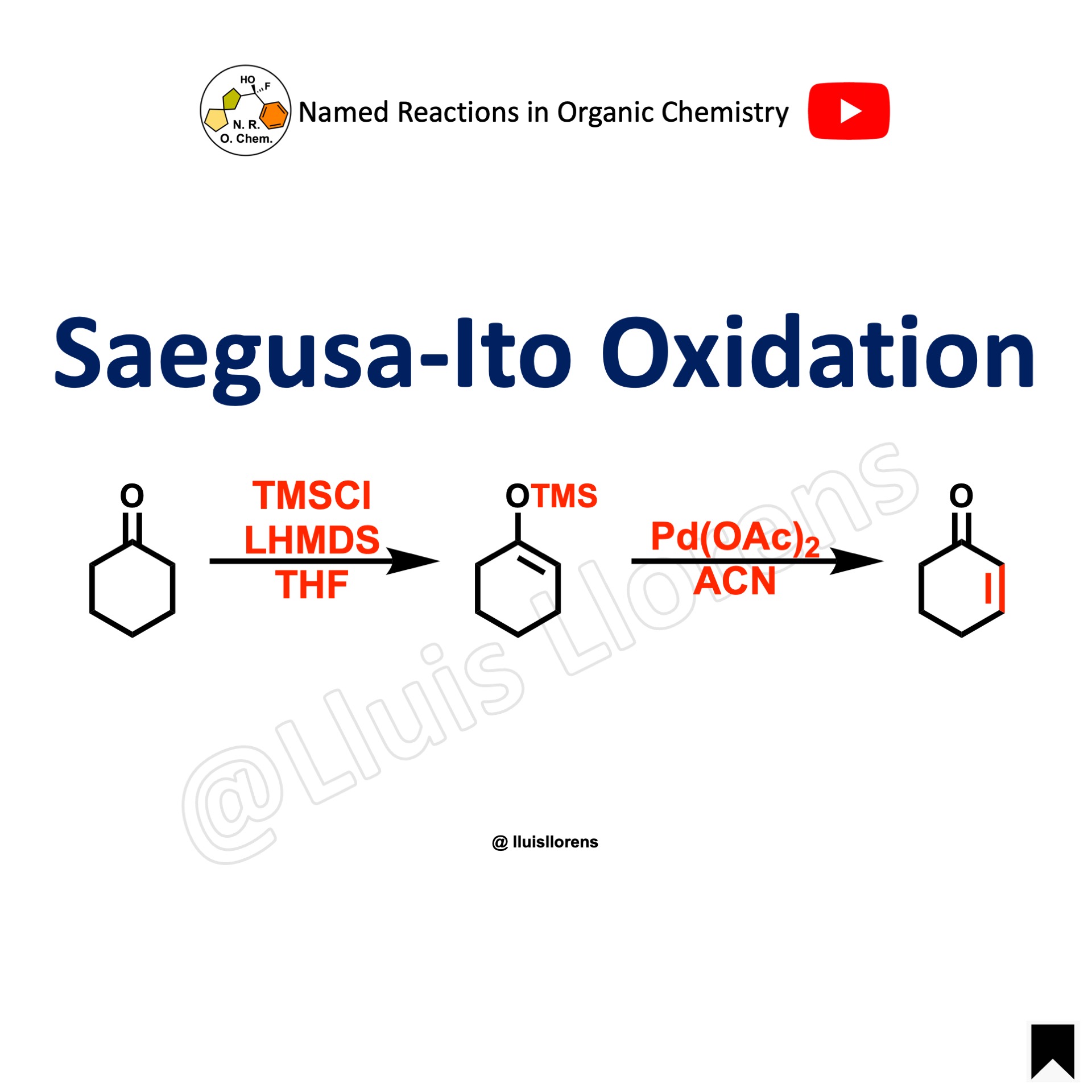
The Saegusa-Ito oxidation allows the regioselective introduction of an alpha, beta C–C double bond to cyclic and acyclic ketones. The reaction involves the formation of a silyl enol ether followed by a Pd-mediated oxidation to the corresponding enone.
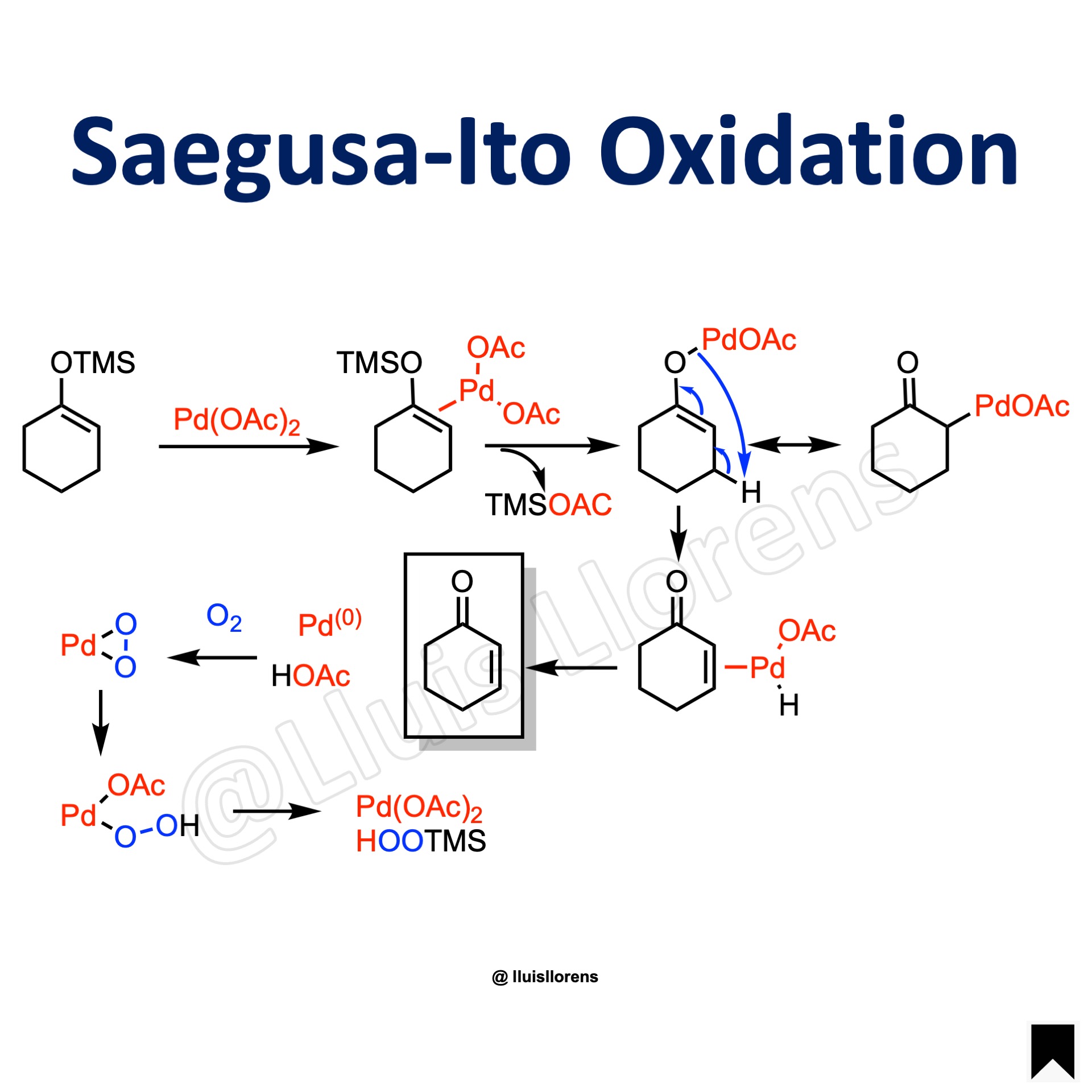
Reaction Mechanism
1. Coordination of palladium to the enol olefin. 2. Loss of the silyl group and formation of the complex. 3. Beta-hydride elimination. 4. Reductive elimination yields the product, acetic acid, and Pd(0). 5. Reoxidation of the catalyst.
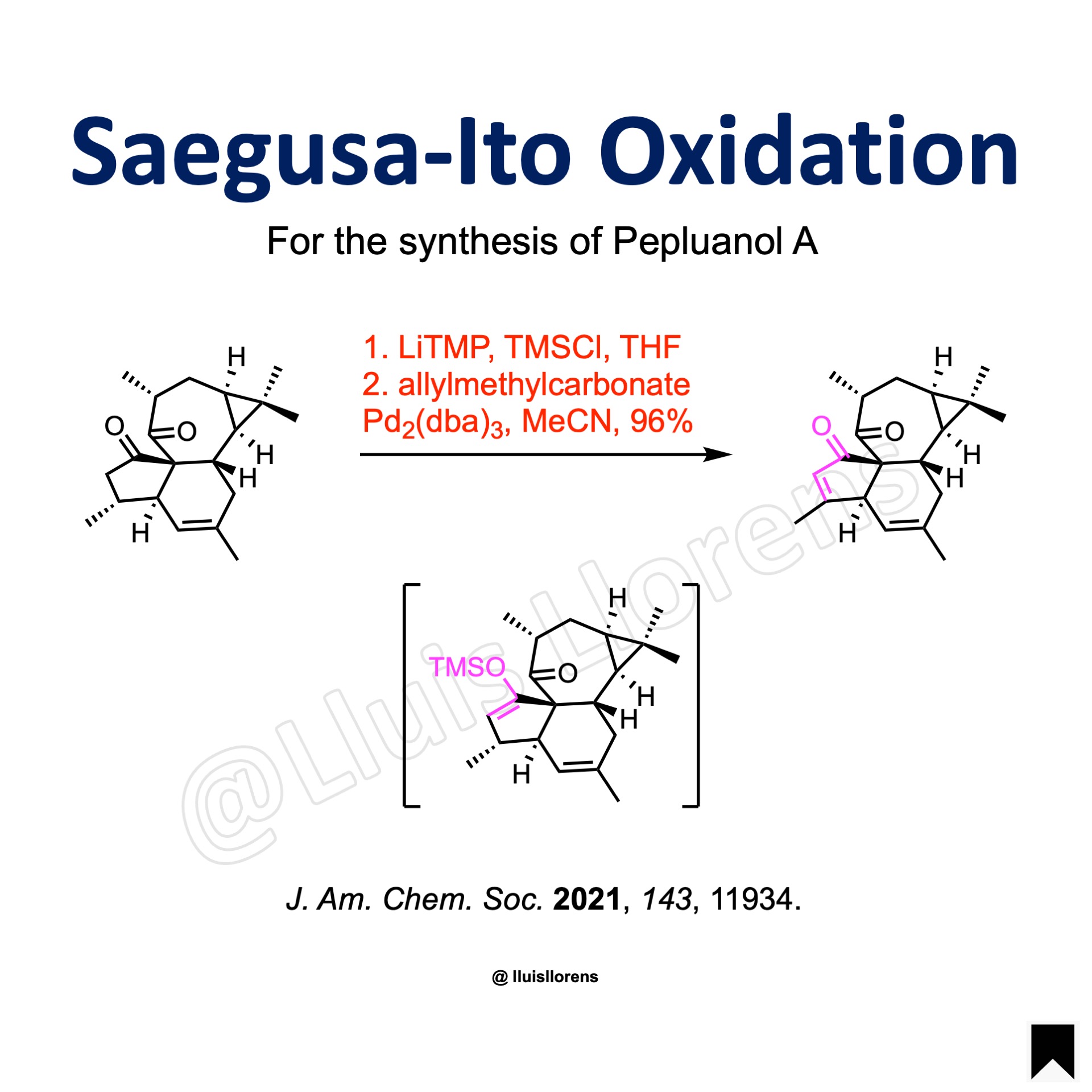
Experimental Procedure
2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine (5.2 equiv) was dissolved in dry THF (20.6 mL). The solution was cooled to -78 ºC, and n–BuLi (2.5 M in hexane, 5.0 equiv) was added dropwise at this temperature. The reaction was kept stirring for 10 min. Then the freshly prepared lithium tetramethylpiperidide was slowly transferred to the stirring solution mixed with the diketone (1.98 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and TMSCl (4.0 equiv) in THF (20.6 mL) via cannula at -78 ºC. After stirring for 30 min, the reaction was warmed to 0 ºC gradually. The stirring was continued for 10 min before it was diluted with pentane and quenched by saturated aq. NaHCO3. Then the reaction was extracted with pentane. The combined organic layers were dried, filtered and evaporated under reduced pressure. The remaining crude TMS-enol ether was re-dissolved in dry MeCN (40 mL). To the above stirring solution, were added tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium(0) (0.20 equiv) in one portion and allyl methyl carbonate (2.0 equiv) dropwise at room temperature. The reaction was allowed to warm to 40 ºC and stirred for 3 h before it was filtered through a short pad of Celite®. The filtrate was collected and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel to give the resulting enone (96% yield).
Learn More Named Reactions
[instagram-feed feed=2]