Pinner Reaction
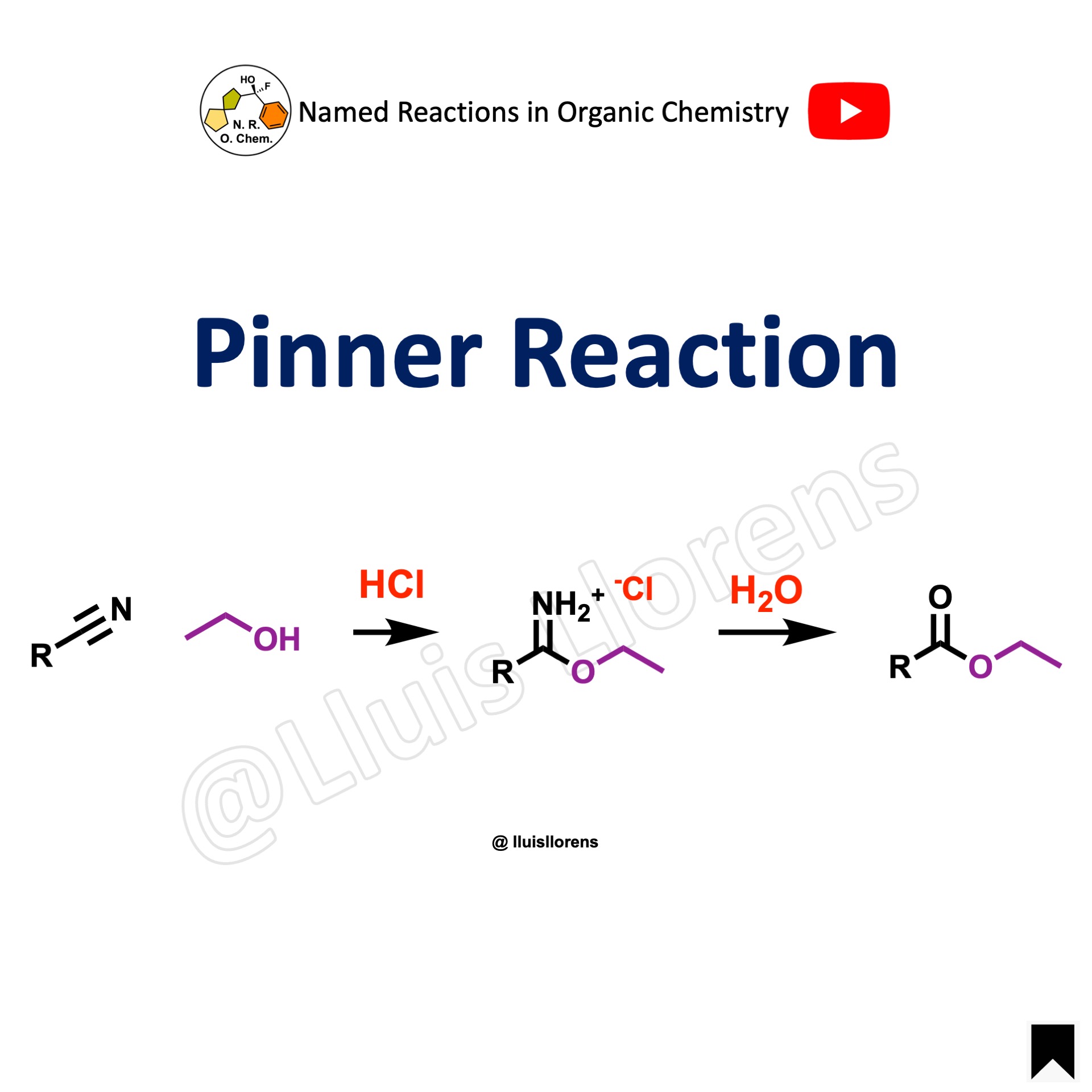
The Pinner reaction is the acid-catalyzed reaction of a nitrile with an alcohol to afford an imino ester salt that may undergo nucleophilic addition with a variety of compounds.
General features:
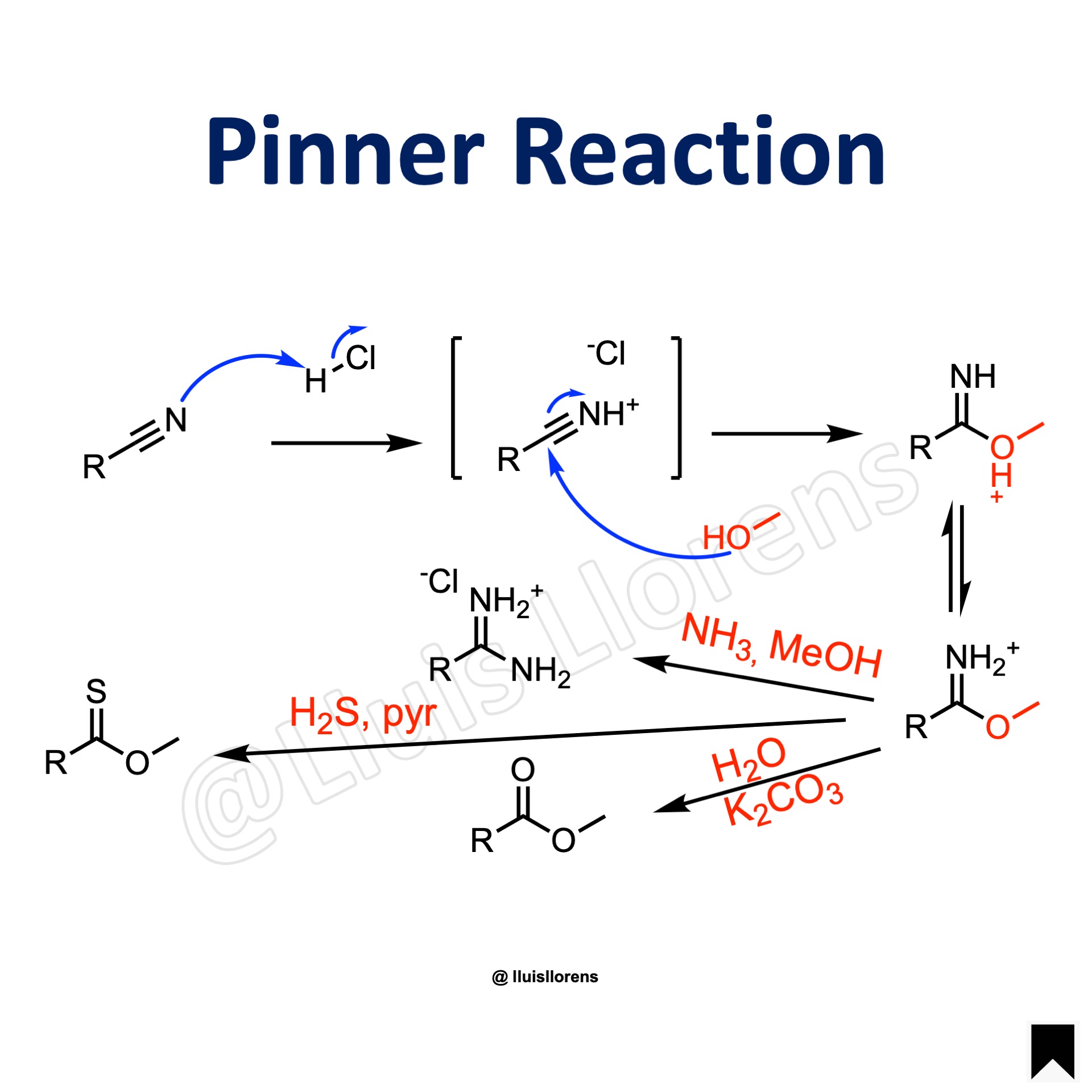
1. The reaction is carried out in anhydrous conditions. Dry hydrogen chloride gas is bubbled through the solution at 0 C° to avoid decomposition of the imino ester salt. 2. A wide range of nitriles can be used. Aliphatic, aromatic, and heteroaromatic substrates are well tolerated, except for sterically hindered nitriles. 3. The imino ester salt undergoes nucleophilic addition with nucleophiles to deliver a variety of compounds: with an excess of alcohol forms an orthoester; with ammonia or an amine delivers an amidine; with water generates an ester; and it also reacts with hydrogen sulfide to form a thionoester.
Reaction Mechanism
1. Treatment of the nitrile with gaseous HCl affords the nitrilium ion. 2. Addition of the alcohol delivers an imino ester salt, a Pinner salt. 3. Further reaction with water delivers an ester; reaction with ammonia forms an amidine, and with hydrogen sulfide a thionoester.
Example
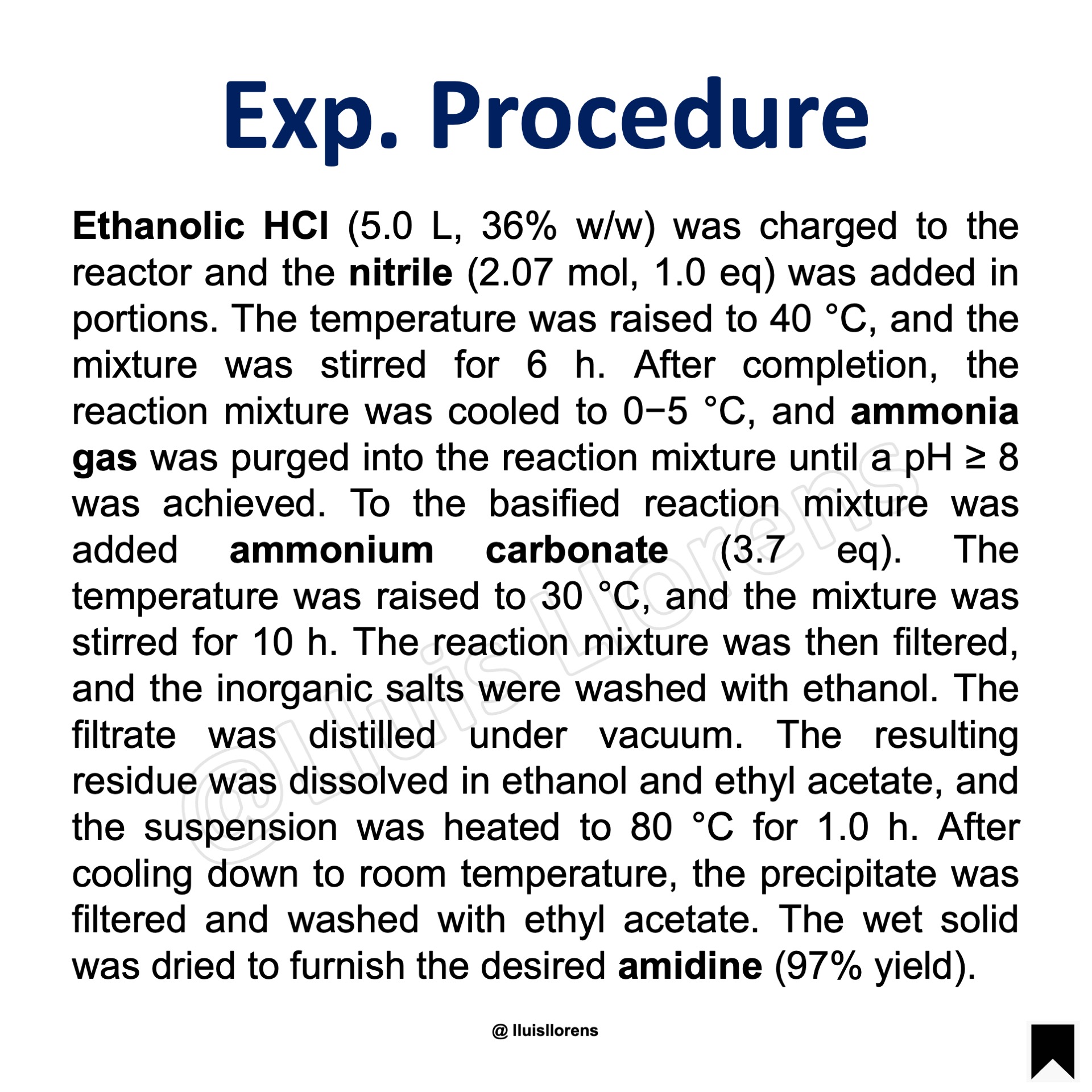
Experimental Procedure
Ethanolic HCl (5.0 L, 36% w/w) was charged to the reactor and the nitrile (2.07 mol, 1.0 eq) was added in portions. The temperature was raised to 40 °C, and the mixture was stirred for 6 h. After completion, the reaction mixture was cooled to 0−5 °C, and ammonia gas was purged into the reaction mixture until a pH ≥ 8 was achieved. To the basified reaction mixture was added ammonium carbonate (3.7 eq). The temperature was raised to 30 °C, and the mixture was stirred for 10 h. The reaction mixture was then filtered, and the inorganic salts were washed with ethanol. The filtrate was distilled under vacuum. The resulting residue was dissolved in ethanol and ethyl acetate, and the suspension was heated to 80 °C for 1.0 h. After cooling down to room temperature, the precipitate was filtered and washed with ethyl acetate. The wet solid was dried to furnish the desired amidine (97% yield).
Learn More Named Reactions
[instagram-feed feed=2]