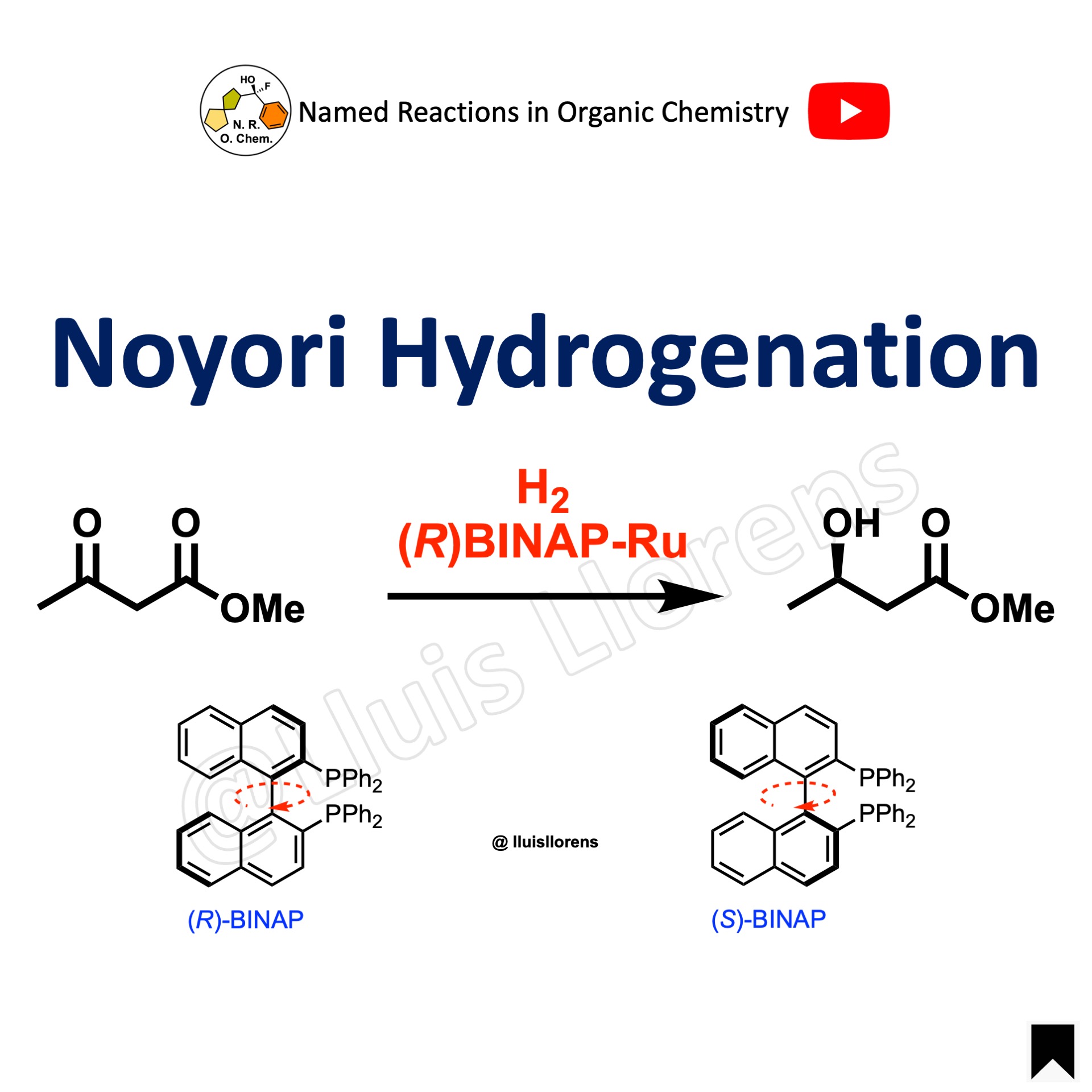
Noyori Hydrogenation
The Noyori asymmetric hydrogenation allows the enantioselective reduction of ketones with hydrogen gas and catalytic amounts of BINAP-Ru(II) complexes.
BINAP is a C2-symmetric chiral ligand that is commercially available in both enantiomeric forms. The molecule doesn’t have any stereogenic atom, but it has axial chirality due to the restricted rotation about the bond that unites the two naphthyl rings. Therefore, (R)-BINAP and (S)-BINAP are atropisomers.
Reaction Mechanism
1. The BINAP-Ru dihalide precatalyst is converted to the catalyst by reaction of hydrogen. 2. The substrate coordinates to the catalyst, and hydrogenation of the keto ester proceeds through the keto form. 3. The product is displaced by the ligands, and the catalyst is regenerated upon reaction with another equivalent of hydrogen.
Example
Experimental Procedure
A Schlenk flask was charged with acetylacetone (315 mmol, 1.0 eq) and EtOH (32.3 mL). The solution was sparged with N2 for 1 hour. In a N2-filled glovebox, the solution of acac in EtOH was transferred to a glass jar and RuCl2[(R)-BINAP] (0.1 mol%) was added. The jar containing the reaction mixture was lowered into a parr bomb, which was then sealed and brought out of the glovebox. The bomb was purged with H2 and then pressurized to 1100 psi, lowered into an oil bath at 30 °C, and secured with a chain clamp. The reaction was stirred for 6 days. The pressure was released and the reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuo. The product was purified by distillation using a short-path distillation head under reduced pressure.
Learn More Named Reactions
[instagram-feed feed=2]