Gabriel Synthesis
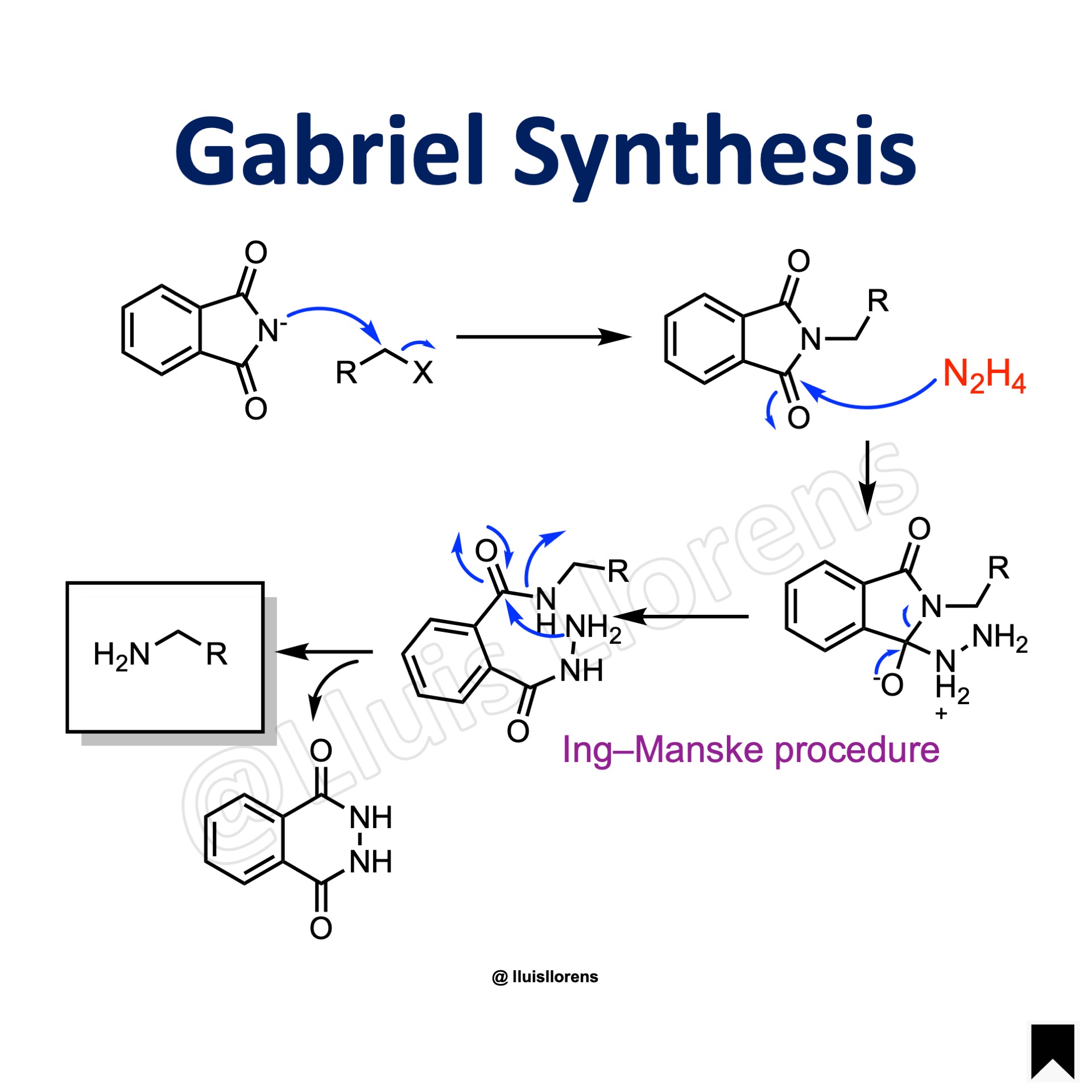
The Gabriel synthesis of amines is the chemical reaction that transforms primary alkyl halides into primary amines in a two-step reaction process.
General features: 1. DMF, DMSO, HMPA, chlorobenzene, acetonitrile, and ethylene glycol are commonly used solvents, being DMF the best (good for SN2 reactions). 2. The best alkylating agents are alkyl sulfonates, α-halo ketones, esters, nitriles, and α,β-unsaturated compounds. Also, sterically unhindered alkyl halides (alkyl iodides being the most reactive) followed by allylic, benzylic, and propargylic halides. And aryl halides in the presence of Cu(I) catalyst. 3. Strong alkaline hydrolysis is often incompatible with base-sensitive functional groups. The use of hydrazine hydrate in refluxing ethanol for the cleavage of the N-alkylphthalimide under mild and neutral conditions is often employed. It is also known as the Ing-Manske procedure.
Reaction Mechanism
1. Alkylation of potassium phthalimide with alkyl halides via SN2 reaction. 2. Hydrazinolysis of the N-alkylphthalimide by nucleophilic addition of hydrazine across one of the carbonyl groups of the phthalimide. 3. Ring-opening, proton transfer, intramolecular SNAc reaction, proton transfer, and breakdown of the tetrahedral intermediate gives the primary amine and phthalyl hydrazide.
Example
Experimental Procedure
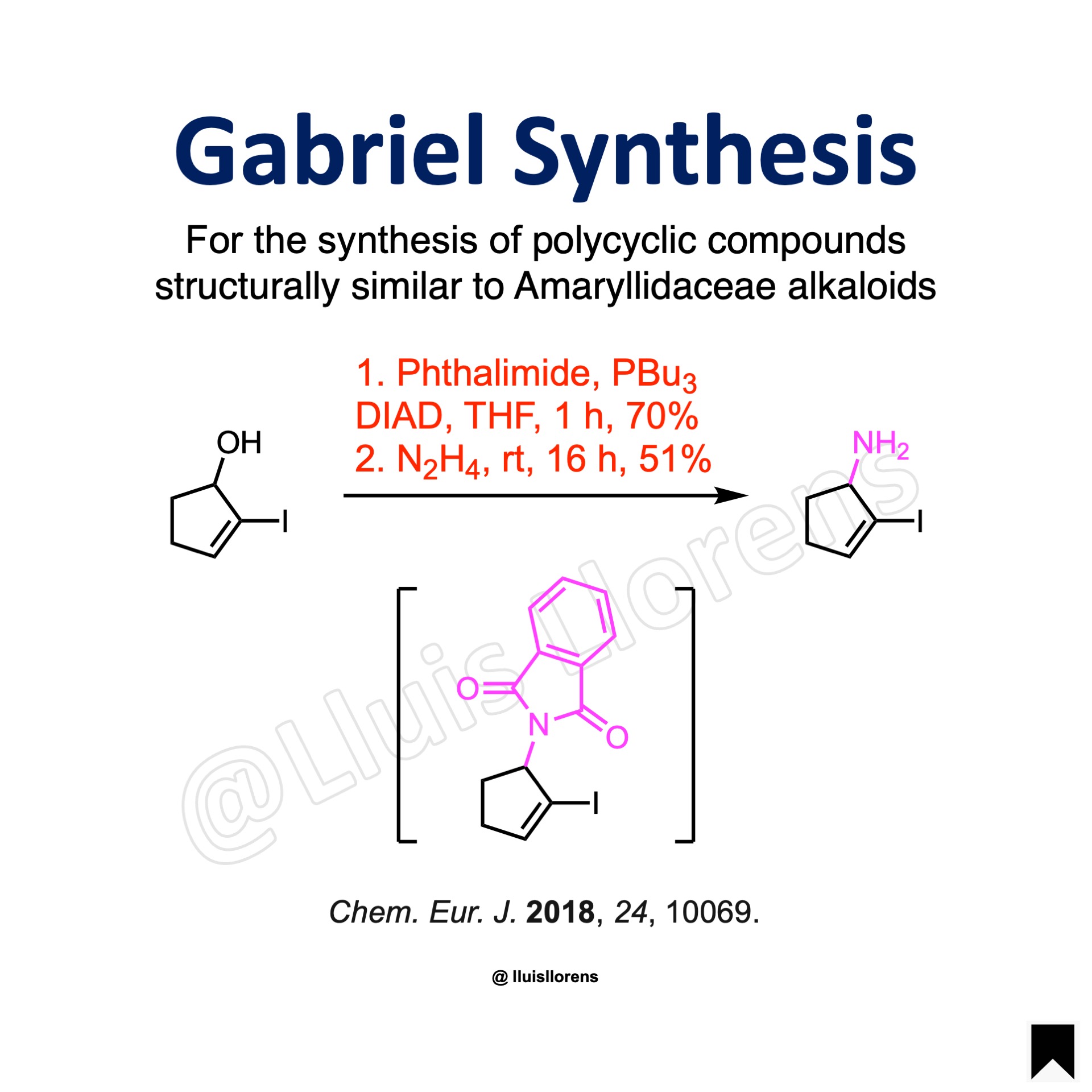
DIAD (1.2 eq) was added to a solution of the alcohol (9.5 mmol, 1.0 eq), phthalimide (1.2 eq), and tributylphosphine (1.2 eq) in dry THF (30 mL) at 0 °C under an argon atmosphere. After stirring at room temperature for 1 h the reaction mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude mixture was purified by column chromatography on silica gel (70% yield).
Hydrazine hydrate (50-60 %, 18.0 eq) was added to a solution of the substrate (2.94 mmol, 1.0 eq) in MeOH (15 mL) under an argon atmosphere, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 16 h. Then reaction mixture was then diluted with diethyl ether, and the formed precipitate was filtered off on celite, and the filtrate concentrated under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel to give the desired amine (51% yield).
Learn More Named Reactions
[instagram-feed feed=2]